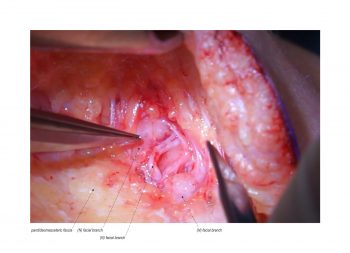
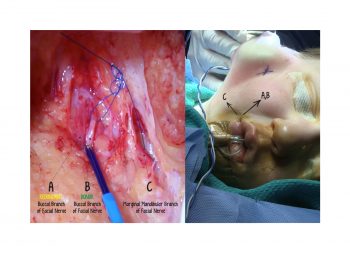
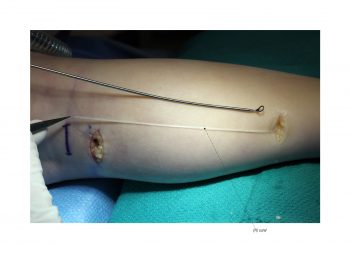
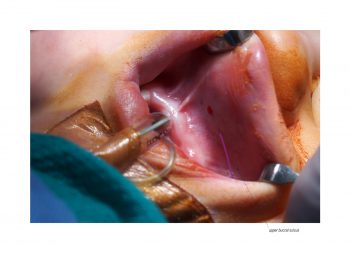
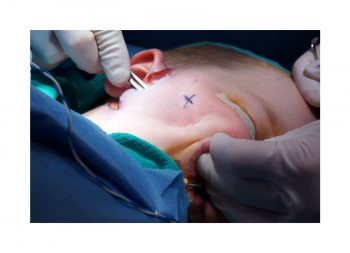
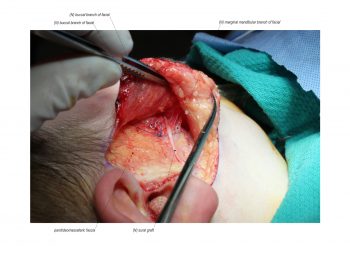
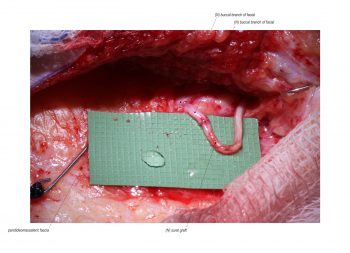
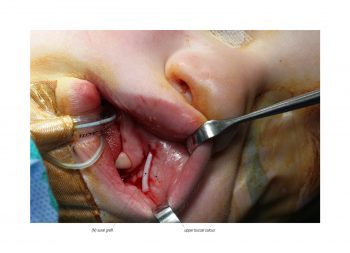
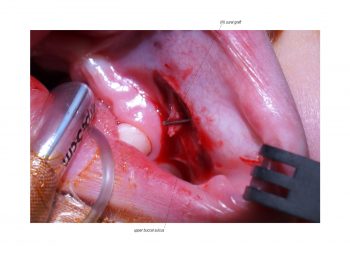
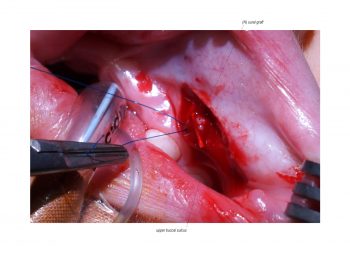
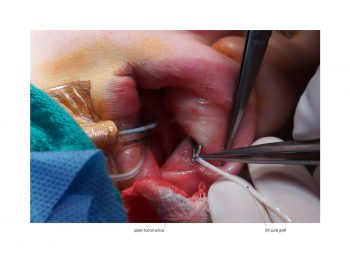
Facial paralysis causes significant morbidity and dynamic reconstruction aims to address functional, aesthetic, and psychological aspects of the impairment. Cross-facial nerve grafting is a reconstructive strategy used to restore smile function and eye closure in both acute and chronic unilateral injury. In an acute injury, nerve grafting provides regenerating fibers from the donor nerve on the normal side to reinnervate across the face to the similar recipient nerve on the paralyzed side. In a chronic injury where the paralyzed muscle can no longer be reinnervated, the cross-facial nerve graft serves as the first stage to a segmental free functional muscle transfer to reconstruct smile. In this case, the patient presented 4-years-ago with a posterior fossa medulloblastoma, which was removed, and underwent a successful course of chemotherapy. However, the tumor involved partial CN12 and complete CN6 and CN7 nerve paralysis on the left side. Reconstruction included a 2-stage segmental gracilis muscle transfer to reconstruct smile with stage one providing the donor nerve source for the muscle. This video details the selection of the donor buccal branch of the contralateral facial nerve and coaptation of the sural nerve graft as the cross-facial nerve graft. The specifics of the sural nerve harvest are not included in this video.
Standard 140520
Extended 140520
POSITION
Supine.
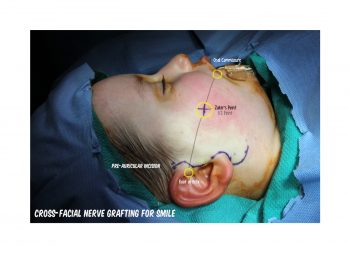
INCISION
Pre-auricular incision.
REFERENCES
- Dorafshar AH, Borsuk DE, Bojovic B, Brown EN, Manktelow RT, Zuker RM, Rodriguez ED, Redett RJ. Surface anatomy of the middle division of the facial nerve: Zuker’s point.Plast Reconstr Surg. 2013 Feb;131(2):253-7. PMID: 23357986.
- Borschel GH, Kawamura DH, Kasukurthi R, Hunter DA, Zuker RM, Woo AS. The motor nerve to the masseter muscle: an anatomic and histomorphometric study to facilitate its use in facial reanimation. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2012 Mar;65(3):363-6. PMID: 21992936.
- Fattah A, Borschel GH, Manktelow RT, Bezuhly M, Zuker RM. Facial palsy and reconstruction. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2012 Feb;129(2):340e-352e. PMID: 22286449.
- Fattah A, Borschel GH, Zuker RM. Reconstruction of facial nerve injuries in children. J Craniofac Surg. 2011 May;22(3):782-8. Review. PMID: 21558887.
- Manktelow RT, Zuker RM, Tomat LR. Facial paralysis measurement with a handheld ruler. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2008 Feb;121(2):435-42. PMID: 18300969.
- Manktelow RT, Tomat LR, Zuker RM, Chang M. Smile reconstruction in adults with free muscle transfer innervated by the masseter motor nerve: effectiveness and cerebral adaptation. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006 Sep 15;118(4):885-99. PMID: 16980848.
- Bae YC, Zuker RM, Manktelow RT, Wade S. A comparison of commissure excursion following gracilis muscle transplantation for facial paralysis using a cross-face nerve graft versus the motor nerve to the masseter nerve. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2006 Jun;117(7):2407-13. PMID: 16772949.
- Ames WA, Shichor TM, Speakman M, Zuker RM, McCaul C. Anesthetic management of children with Moebius sequence. Can J Anaesth. 2005 Oct;52(8):837-44. PMID: 16189336.
- Singham J, Manktelow R, Zuker RM. Möbius syndrome. Semin Plast Surg. 2004 Feb;18(1):39-46. doi: 10.1055/s-2004-823122. PMID: 20574469.
- Goldberg C, DeLorie R, Zuker RM, Manktelow RT. The effects of gracilis muscle transplantation on speech in children with Moebius syndrome. J Craniofac Surg. 2003 Sep;14(5):687-90. PMID: 14501329.
- Zuker RM, Goldberg CS, Manktelow RT. Facial animation in children with Möbius syndrome after segmental gracilis muscle transplant. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2000 Jul;106(1):1-8; discussion 9. PMID: 10883605.
- Zuker RM, Posnick JC. The role of microsurgery in pediatric craniofacial reconstruction. Clin Plast Surg. 1992 Oct;19(4):833-9. Review. PMID: 1339639.
- Zuker RM. Facial paralysis in children. Clin Plast Surg. 1990 Jan;17(1):95-9. PMID: 2302922.
- Zuker RM, Manktelow RT. A smile for the Möbius’ syndrome patient. Ann Plast Surg. 1989 Mar;22(3):188-94. PMID: 2735718.
Disclosure: No authors have a financial interest in any of the products, devices, or drugs mentioned in this production or publication.